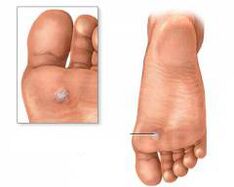
PlantarWartsare benign growths of epithelial cells in the form of small growths that are caused by the human papillomavirus. These manifestations are localized directly on the support areas of the foot or toes.
Interesting facts:
- According to statistics, the manifestation of plantar warts is most often observed between the ages of 20 and 30 years.
- In most cases (more than 50%) plantar warts can heal on their own without treatment.
- According to various sources, carriers of HPV (human papillomavirus) make up 70 to 90 percent of the world's population.
- Plantar warts are popularly called "spines". This interpretation is associated with thorns, which it is painful to enter.
- Most types of HPV affect the skin.
Causes of warts
A wart is a viral skin disease caused by the human papillomavirus.
There are about a hundred varieties of this virus. They can penetrate the human body and do not show themselves for a long time, thanks to such protective properties of the body as:
- immunity;
- Phagocytosis (is an unspecific defense reaction of the body, ie when a pathological agent enters the body, phagocytes surround it and destroy it).
The risk of infection with human papillomavirus depends on the following factors:
- virus activity in a human carrier;
- Type of contact (direct or indirect contact);
- the immunity level of an infected person.
70 - 90% of people are carriers of the human papillomavirus. However, whether or not a wart appears depends on the state of immunity. People whose body resistance is decreased are more prone to the manifestation of warts. In addition, the risk of developing warts increases in cases where the body is affected by adverse factors (, e. g. B. stress, tiredness, insomnia, poor hygiene) is affected, which lead to a weakening of the immune system.
The papillomavirus can be spread through contact with a person with warts, e. g. B. by handshake, common objects (towel, slippers);
There are the following predisposing factors for infection with human papillomavirus:
- sweating of the legs (the skin becomes looser and the penetration of various infections is made easier);
- Frequent washing, cleaning (Frequent skin irritation with various cleaning agents destroy the protective barrier of the skin and thus make it easier for the virus to penetrate)
- microtrauma of the skin or mucous membrane (cracks, scratches, abrasions are the gateway for infections that get into the body);
- uncomfortable tight shoes that cause the skin of the feet to rub (calluses, abrasions are also a gateway for infections that get into the body);
- diseases that lead to malnutrition of the foot epithelium (for example diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis); A
- virus infection can occur through pedicure tools (if the devices have not been disinfected).
- public baths, saunas or swimming pools (places where the feet come into direct contact with a possibly infected floor surface).
The human skin consists of epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous fat. The human papillomavirus, which penetrates the skin tissue, affects the base layer of the epidermis. The cells affected by the virus then multiply through all layers of the epidermis and are located on the superficial stratum corneum of the epithelium, which manifests itself externally in rough and keratinized skin.
Human papillomavirus
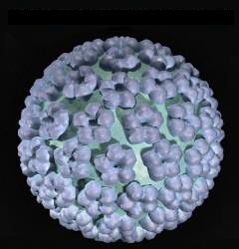
HPV is an infection of the papovavirus family that affects the mucous membranes of the organs (usually the genitals) and the epithelial cells of the skin. The papillomavirus contains DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) which, when introduced into a cell in the human body, causes the production of new virus particles.
All HPV types can be roughly divided into two groups:
- papilloma viruses with oncogenic properties;
- Papilloma viruses that do not have oncogenic properties.
Note:oncogenic properties contribute to the formation of malignant tumors.
Today there are more than a hundred types of human papillomavirus. Plantar warts are usually caused by the first type of HPV, in some cases their formation can cause the second and fourth types (non-oncogenic papilloma viruses).
HPV is common in anyone who has sex. All eight out of ten people are infected with this virus. Of all HPV types, 6, 11, 16, and 18 are classified as the most dangerous. These types of HPV can cause papillomas, condylomas, and cancer.
Symptoms and what warts look like on the feet
The human papillomavirus that invades tissues can be in a passive or active state.
- The passive state is characterized by the fact that the virus slowly multiplies in the base layer of the epidermis and does not reach the stratum corneum of the epithelium. Therefore, this state does not manifest itself outwardly.
- An active state is characterized by the fact that the virus is actively developing and manifesting itself in the upper layers of the epidermis with numerous symptoms.
| Show | Photo | |
| Shiny surface | First the plantar wart appears as a shiny plaque, then its surface becomes keratinized and rough and coarser. | 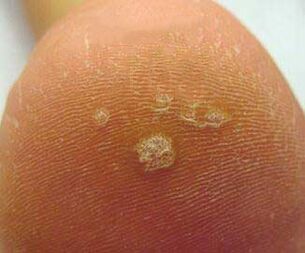 |
| Dimensions | Plantar warts are between one and two centimeters in size and protrude one to three millimeters above the surface of the epithelium. Most often, warts are oval or round. There is also the concept of the mother and daughter wart. The maternal wart appears first and is the largest, usually smaller daughter warts can form around it. Over time, mother and daughter warts can combine into large lesions. | |
| Pain | The plantar wart is on the foot where most of the weight is. The wart is compressed between the sole and the bone, making the surrounding tissue hard. These warts are very painful in most cases as the wart can compress the nerves in the foot and cause pain when you walk. | |
| color | Most warts are light brown or yellow-white in color. | |
| Blackheads | When the stratum corneum is removed from the surface of the wart, dark spots may appear on the bed of the affected area, which form due to the fact that the bleeding capillaries in that area are thrombosed. This symptom is a distinctive feature of the plantar wart versus callouses and calluses. |
Removal of warts on the sole
There are currently many effective and safe treatments for plantar warts. It should be noted, however, that in some cases, reliable wart removal is made difficult by the fact that the human papillomavirus penetrates the deepest layers of the epidermis (in the base layer).
Treatment of a wart is required if:
- the wart hurts;
- the wart is bleeding;
- large wart;
- the wart color is uneven (, for example, spots appeared in it);
- There is a rapid growth dynamic of the wart.
There are the following methods to remove plantar warts:
- cryodestruction;
- laser coagulation;
- electrocoagulation;
- radio wave surgery;
- surgical removal.
Cryodestruction
With this method, the wart is exposed to liquid nitrogen at a temperature of minus 196 degrees. Cryodestruction is characterized by the fact that when the wart is frozen, the skin area affected by the virus is destroyed, followed by the stimulation of the body's own immune system. However, it should be noted that if the wart appears and persists for up to six months, the effectiveness of its removal is 84%. While the effectiveness of removing warts that persist for more than six months is reduced to 39%.
Cryodestruction procedures can be performed:
- usually (liquid nitrogen is applied until a light halo two millimeters in diameter appears around the wart);
- aggressive (after a slight halo has appeared around the wart, liquid nitrogen is used for another five to twenty seconds).
Research has shown that the aggressive method of freezing the wart is more effective than the traditional method, but the disadvantage is that it is more painful.
After removal of the wart at the exposure site, there is hyperemia (reddening) of the skin, followed by the formation of edema. A few hours later, a blister forms on the affected area (may contain hemorrhagic or serous fluid), and about six to seven days after the blister dries, a crust forms on its site, which within twoWeeks to disappear on its own.
After removing the wart, follow these guidelines:
- A blister formed at the site of the wart should not be opened.
- The affected area should not be covered with tape.
- It is recommended to bandage the exposure site with a sterile bandage without tightening it to avoid mechanical damage and contamination of the affected area.
- It is recommended to treat the affected area with 2% salicylic alcohol twice a day.
- try to avoid the ingress of water at the exposure site.
| Disadvantages of the method | |
| Tissue heals without scars | If exposure to liquid nitrogen occurs superficially, there is a high likelihood of recurrence (reformation) of warts |
| The process is carried out without local anesthesia | After the procedure | Local hypo- or hyperpigmentation can occur
| Removing a wart with this method takes one to two minutes | If deep cauterization occurs, there is a risk of scarring |
Laser coagulation
Removing warts with a laser beam is one of the most common treatment methods today. This method is characterized by a layer-by-layer burn of the affected area, which allows you to control the exposure depth. When removing a wart, the laser beam simultaneously brazes the vessels, which prevents bleeding from developing at the site of exposure.
The following laser coagulation methods are available:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) laser.The wart is exposed to infrared light (the wavelength is 10 600 nm). The disadvantage of this method of treatment is that the cauterization of the tissue is not selective, that is, there is a possibility of damage to healthy tissue. The efficiency of removing plantar warts with a carbon dioxide laser is 70%.
- erbium laser.This method is characterized by a shorter wavelength of 2940 nm, which significantly reduces the likelihood of scarring after tissue epithelialization. The effectiveness of this method of treatment is 75%.
- Pulsed dye laser.This method is characterized by the selective absorption of oxygenated hemoglobin (wavelength is 586 nm), at which the destruction of enlarged capillaries in the wart occurs, as well as by the stimulation of the immune system, resulting in acontributes to effective healing. The effectiveness of this treatment method is approx. 95%.
After the laser treatment, a crust forms on the affected area, which disappears by itself within seven to ten days. It is not recommended to tear off the crust and smear it with something (ointments, creams, alcohol solutions). In addition, water should be avoided at the exposure site for the first few days after the procedure.
| Disadvantages of the method | |
| Tissue heals without scars | The only disadvantages of this method are the high costs of the procedure |
| fast healing of the tissue | |
| low risk of repetition (repetition) | |
| hardly affects healthy tissue |
Electrocoagulation
A plantar wart is exposed to a high frequency current. The affected area should be cauterized under local anesthesia. Thanks to a coagulation loop that is applied to the affected area of the skin, an electric current is applied to the wart, causing death. Also, exposure to high temperatures leads to soldering of the vessels, which prevents the development of bleeding.
After the procedure, a dense crust forms at the exposure site, which disappears by itself within ten days.
After removing the wart, follow these guidelines:
- Try to avoid water or soap on the affected area of skin during the healing phase.
- The crust that has formed must not be touched or torn off.
- For the first seven to ten days, it is recommended that the exposure site be treated with an antiseptic once or twice a day.
| Disadvantages of the method | |
| available costs for the procedure | for small, flat warts |
| prevents bleeding | If you are exposed to deep layers of skin after the tissues have healed, a scar can be left behind. |
| The process takes a few seconds to a minute. | Removing superficial warts can cause them to recur. |
Radio wave operation
This treatment method consists in the use of a special electrode that emits high-frequency radio waves (3, 8 - 4, 0 MHz). Exposure of the plantar wart to high temperatures leads to evaporation of the cells affected by the papilloma virus. Due to the chemical burns of the blood vessels, using this method also prevents bleeding from developing. After exposure, a crust forms on the affected skin area that disappears on its own within seven to ten days.
Contraindicated during the healing phase:
- During the first two days after the procedure, you should not wet the area of the moxibustion.
- peel the crust off within seven to ten days.
| Disadvantages of the method | |
| If healthy tissue is exposed to the affected area, it is virtually unaffected | high costs of the procedure |
| There is only a minimal risk of scarring after the tissue has healed | |
| low risk of remission after treatment (two to five percent) |
Surgical removal
This method is characterized by removing the wart with a scalpel under local anesthesia. Stitches are placed after the affected area is removed and removed after seven to ten days.
| Disadvantages of the method | |
| is used to remove large warts | Scars can remain in the affected area after stitches are removed |
| There is a risk of remission (Disappearance of symptoms) warts |
General principles for the care of the affected skin area after the wart removal:
- If a crust forms, it must not be touched or torn off.
- limit water entry to the affected area;
- After removing the wart, it is impossible to expose the place to direct sunlight.
- No cosmetic products (such as cream or lotion) should be applied to the affected area of the skin.
- It is not recommended to visit public saunas, baths, or swimming pools one to two months after removing the wart.
- After removing the wart, it is recommended to use vitamins A, C and E, as these promote the rapid regeneration (healing) of the tissue and also stimulate the body's defenses.
Note:If complications arise after removing the wart (inflammation of the affected area, prolonged healing, scarring), you should contact your doctor as soon as possible.
Contraindications for all treatment methods are:
- Diabetes mellitus;
- presence of malignant tumors;
- pregnancy;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases near the wart;
- aggravation of herpes;
- increased body temperature;
- high blood pressure (over 140 per 100 millimeters of mercury).
Treating warts without surgery
For single and flat plantar warts, traditional treatment methods are recommended.
| Cooking | Apply | |
| Acetic acid | You need to buy 70% acetic acid and petroleum jelly and prepare a pipette to use the correct dosage. | Before using acetic acid, apply petroleum jelly to healthy skin around the wart. Then a drop of acetic acid should be applied to the wart with a pipette. This method should be used once a day until the wart disappears. |
| Garlic infusion | It is necessary to chop three cloves of garlic, and then pour the resulting mass of boiling water (50 ml). After an hour, the resulting infusion must be filtered and used. | Lubricate the wart area with the resulting infusion once a day until the formation disappears completely. |
| Saline solution | Dissolve a tablespoon of salt in warm water (100 ml) and add a tablespoon of vinegar (9%). The resulting solution must be thoroughly stirred, and then the pulp of a plum should be dipped in it and infused for two hours. After the time has passed, it is necessary to remove the plum from the solution and grind it into a pulp. |
The resulting plum pulp must be applied to the wart. To ensure a secure fit, wrap your foot and put on a sock. This compress should be left on for two to three hours. The process should be repeated every day until the wart is completely gone. |
| Wormwood infusion | Put three tablespoons of dry wormwood in a glass of hot water (250 ml), cover and let steep for two hours. |
The resulting solution should be applied to the affected areas of the foot three to four times a day until the warts resolve. |
| Lemon peel infusion | You need to remove the peel from two lemons and place them in a crushed 1 liter glass. Then add 100 ml of 9% vinegar to the jar and close the jar with a tight lid. The contents should be infused for a week, shaking the jar regularly. At the end of the period, the infusion must be filtered. | The resulting infusion should be moistened with warts twice a day until they are completely gone. |
| St. John's wort decoction | For a glass of water (250 ml) add a tablespoon of chopped St. John's wort and simmer for 15 minutes over low heat. After boiling, the broth needs to be cooled, and then filtered. | With the resulting broth, you will need to lubricate the warts three to four times a day until they are completely gone. |
| Note:In the event of side effects, you should consult your doctor immediately. | ||
Currently, celandine is also used effectively in the treatment of plantar warts. This plant has a yellow-orange medicinal juice.
Celandine has the following medicinal properties:
- bactericidal (causes the death of hidden microorganisms);
- anti-inflammatory;
- antispasmodic;
- choleretic;
- antiviral;
- wound healing;
- cauterizing;
- anti-itch;
- Celandine also contains vitamins A and C.
When treating plantar warts, fresh celandine juice is used, which must be rubbed onto the affected skin two to three times a day until the warts have completely disappeared. Before applying celandine, it is recommended to thoroughly steam the feet in hot water and remove the keratinized part of the wart with a pumice stone.
In the treatment of plantar warts, celandine has the following therapeutic effects:
- helps relieve pain when walking;
- accelerates the drying of the wart and the formation of a crust; Due to the vitamin A and C content,
- stimulates local immune responses.
Celandine also contains various acids (ascorbic acid, succinic acid, malic acid, citric acid) to which HPV is sensitive.
To improve the effectiveness of the treatment of plantar warts, the following recommendations should be observed:
- , to perform daily hygiene procedures for the feet;
- Vitamins should be used regularly to strengthen the immune system (, e. g. vitamins A, E, C).
- use individual footwear (, e. g. slippers);
- With dry foot skin, moisturizing and nourishing foot creams must be used regularly.
- in public places (bath, sauna or swimming pool) personal slippers should be used and avoided barefoot;
- choose the right footwear carefully (for example the right size, natural materials);
- If the feet sweat excessively, desiccants must be used and an attempt must be made to choose shoes according to the weather.

























